Interview Questions
Basic
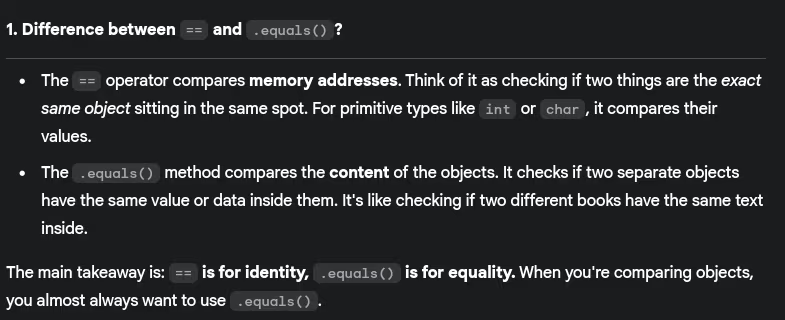
- Difference between == and .equals()?
- What is Java and why is it platform-independent?

- Explain JDK, JRE, and JVM. What are their differences?

- What is bytecode in Java?

- Difference between compiled and interpreted languages. Where does Java fit?

- What is the significance of
public static void main(String args[])in Java?
- What is the significance of
finalkeyword?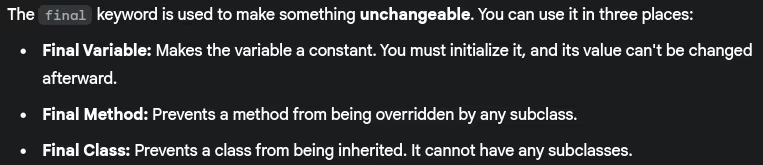
- What is the
statickeyword and its uses?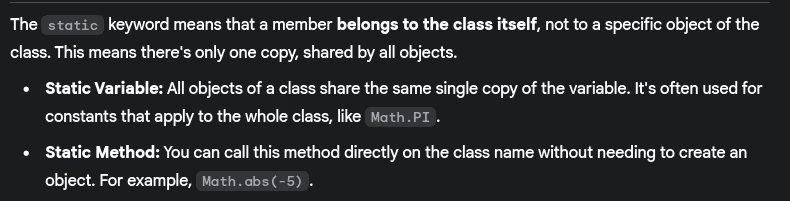
- What is the
volatilekeyword in Java?
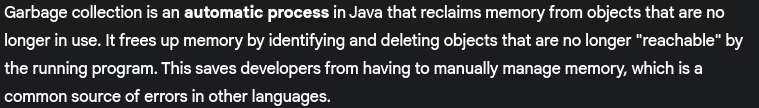
- What is garbage collection in Java?
- How garbage collection works? Algorithm?

- Types of garbage collectors

- What is memory leak in Java?

- What is finalize() method?
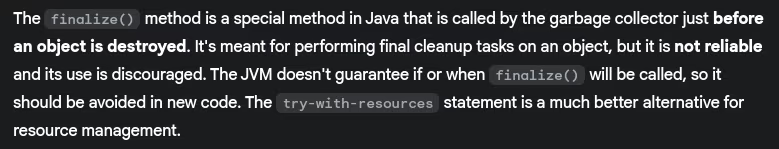
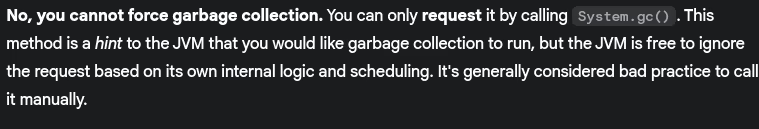
- Can we force garbage collection?
- What is the difference between stack and heap memory?

- What is serialization in Java?

- How JVM works internally?

- How java compilation works?

- Difference between call by value and call by reference? Which one is Java?

- Why new keyword will create anything in heap?

Datatypes
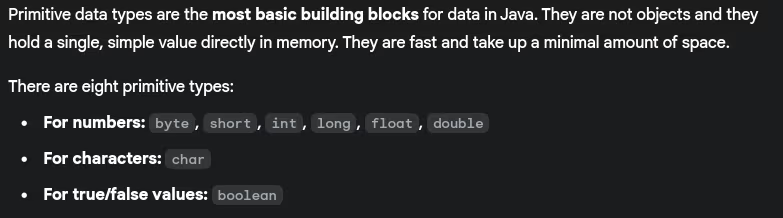
- What are primitive data types in Java?
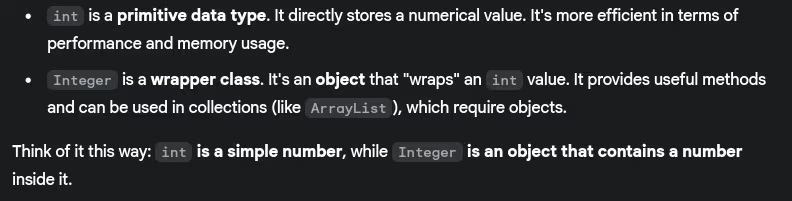
- Difference between int and Integer in Java
- What is autoboxing and unboxing?
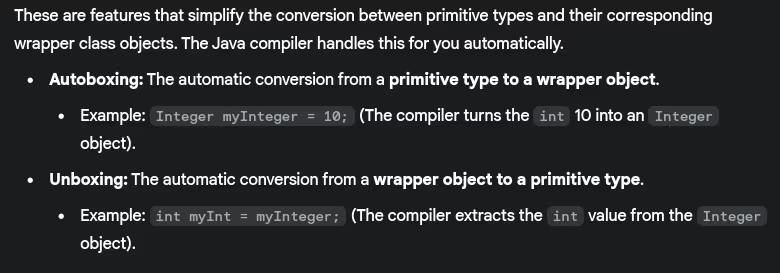
- Explain wrapper classes in Java

- What are the size ranges for different primitive types?

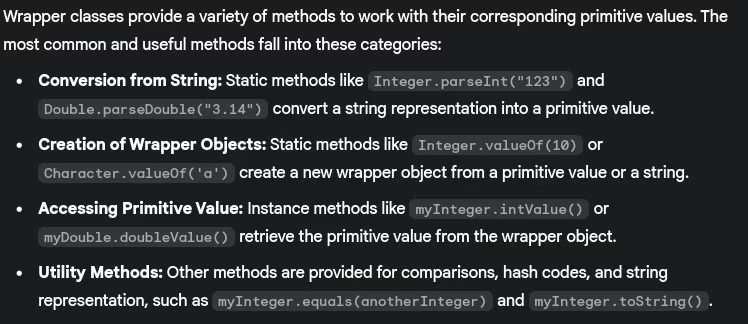
- What are the methods provided by wrapper classes?
Conditional/Control Flow Statements
- What is the difference between
if-elseandswitchstatements?
- When would you use a
switchstatement instead of multipleif-elsestatements?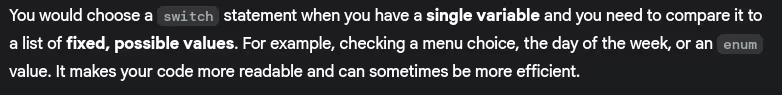
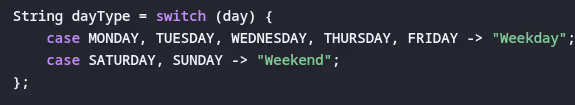
- Can you use a
switchstatement with String values? Since which Java version?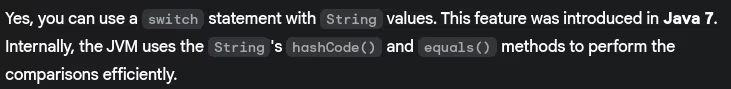
- What's new in switch expressions (Java 14+)?

- What happens if you don’t use
breakin a switch case?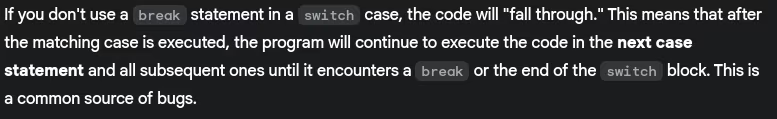
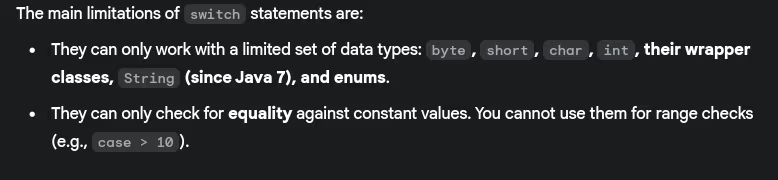
- What are the limitations of switch statements?
- Explain the difference between
whileanddo-whileloops.
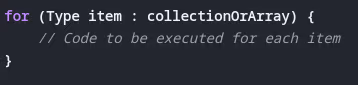
- What is an enhanced for loop (for-each)? When would you use it?


- How do
breakandcontinuestatements work in nested loops?
Strings
- Why are Strings immutable in Java? What are the advantages?

- What's the difference between
String,StringBuffer, andStringBuilder?
- How does string comparison work with
==vsequals()method?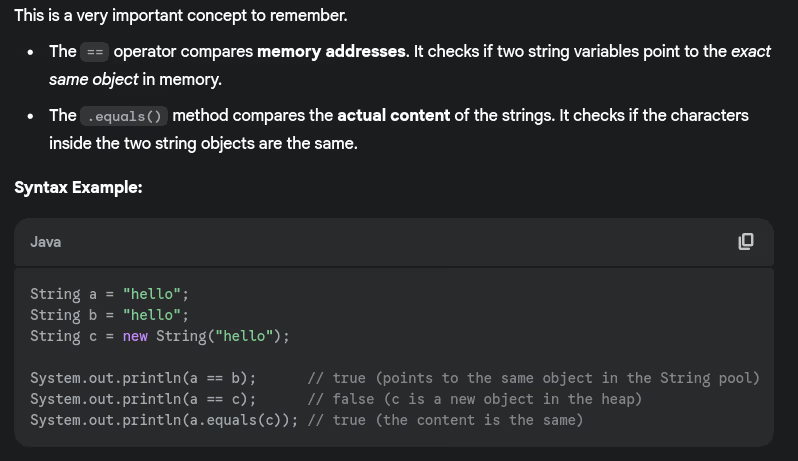
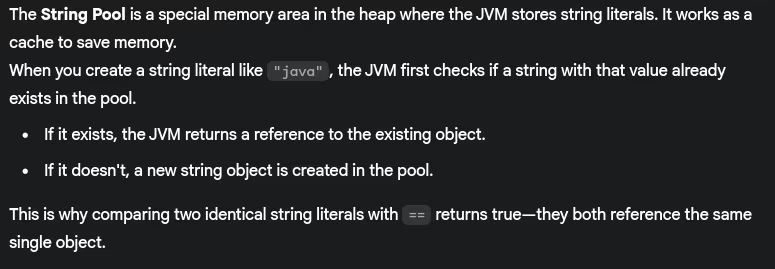
- What is String pool and how does it work?
- What’s the difference between
substring()andcharAt()methods?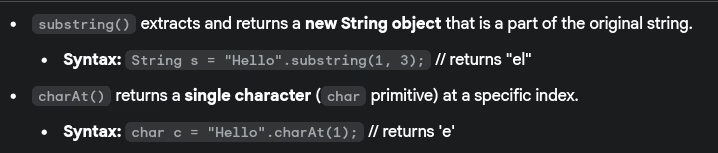
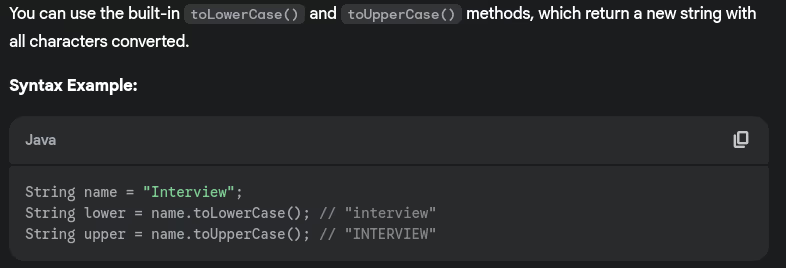
- How do you convert String to lowercase/uppercase?
- What is the trim() method?
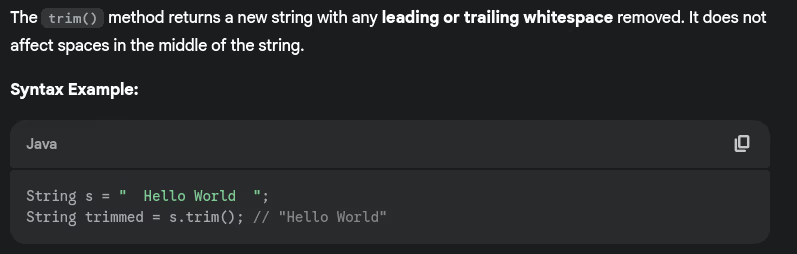
- How do you replace characters in a string?
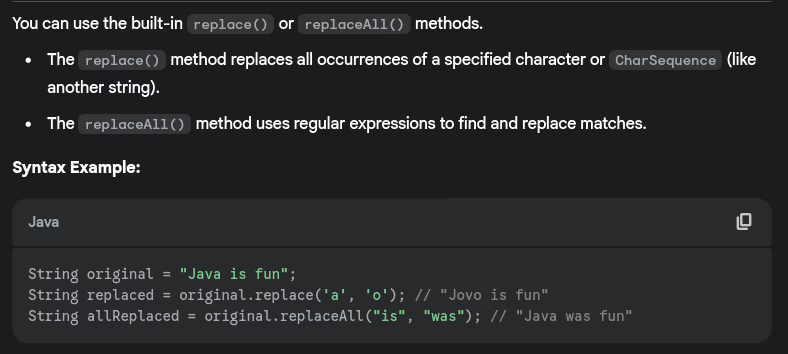
- How do you convert int to String and vice versa?
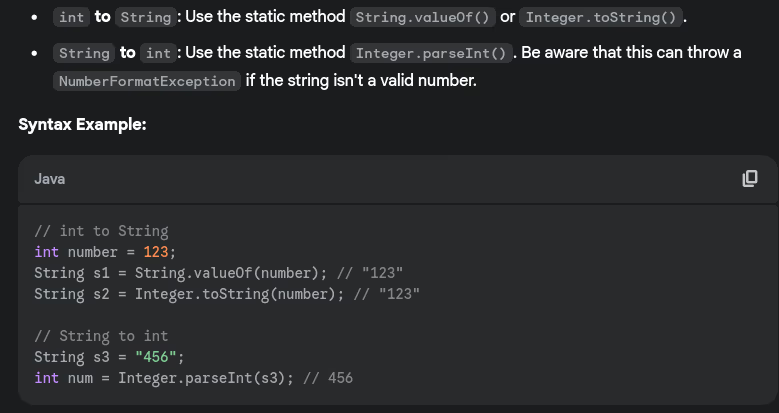
- How do you split a string in Java?
- How do you join strings in Java?
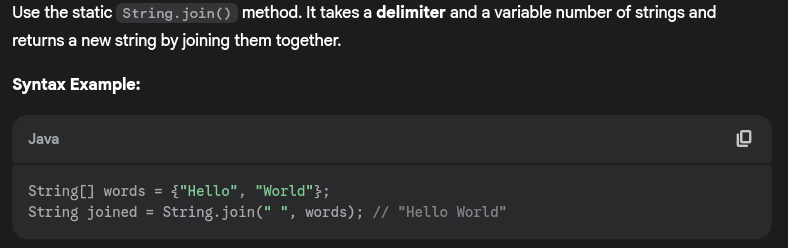
- How do you remove spaces from a string?
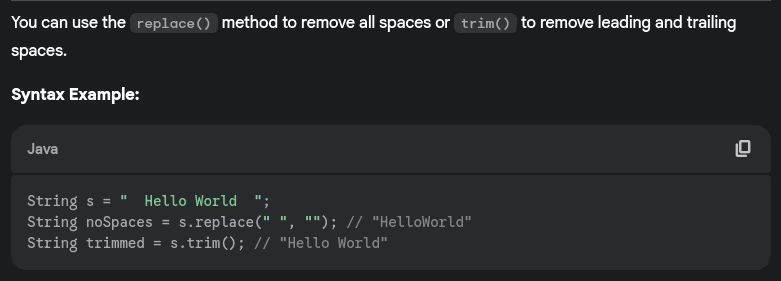
- How do you find the occurrence of a character in string?
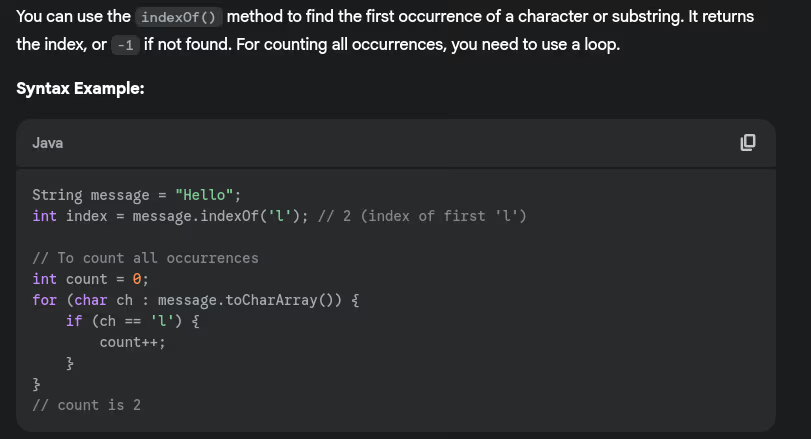
- Common String methods?

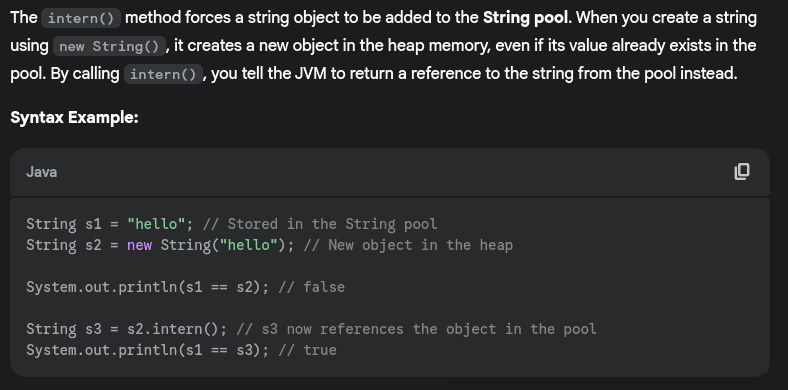
- Explain string interning in Java.
Arrays
- What’s the difference between arrays and ArrayList?

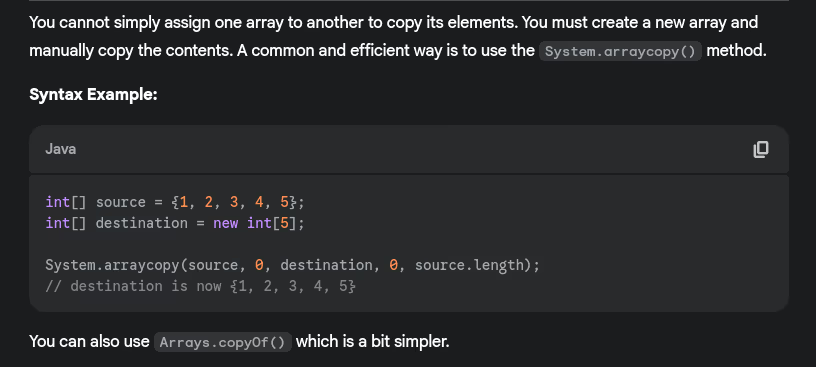
- How to copy arrays?
- How do you find the length of an array vs length of a string?

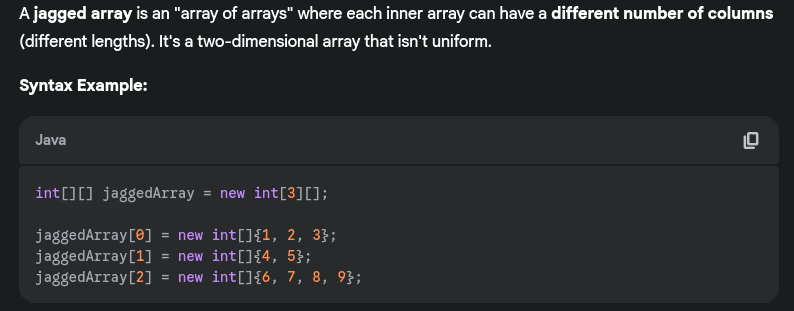
- What are jagged arrays? How do you create them?
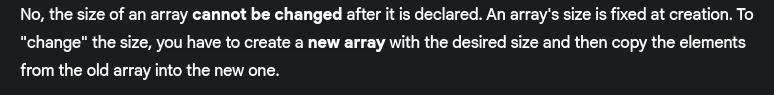
- Can array size be changed after declaration?
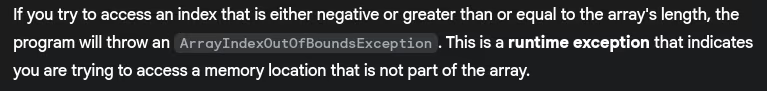
- What happens when you access an array index out of bounds?
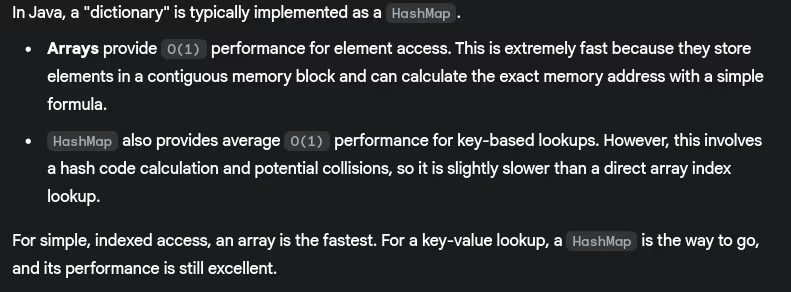
- What is the difference between a dictionary and array in terms of performance?
Date And time
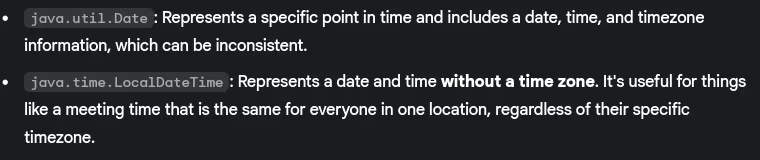
- What’s the difference between
DateandLocalDateclasses?
- Difference between Date and LocalDateTime?
- Which package contains the new Date-Time API introduced in Java 8?

- How do you format and parse dates using
DateTimeFormatter?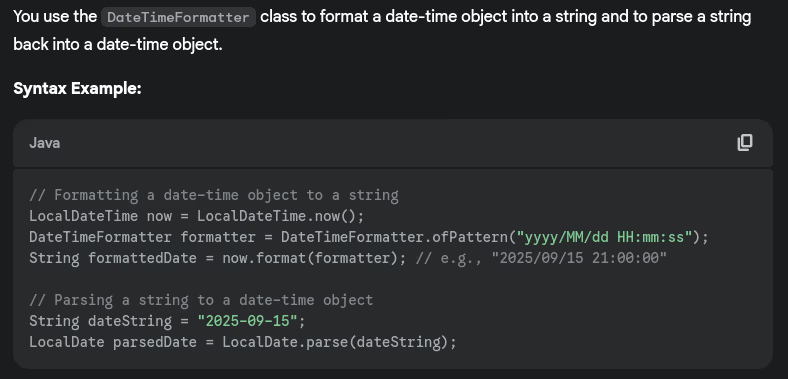
- What are the main classes in
java.timepackage?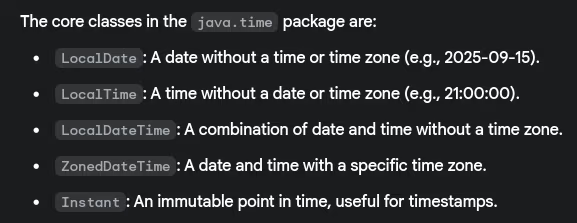
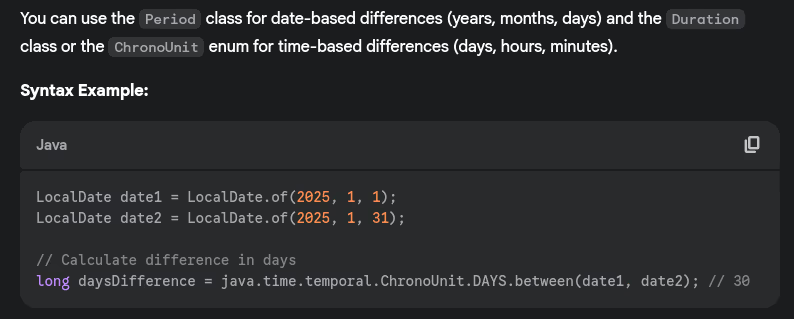
- How do you calculate the difference between two dates?
- What is
ZonedDateTimeand when would you use it?
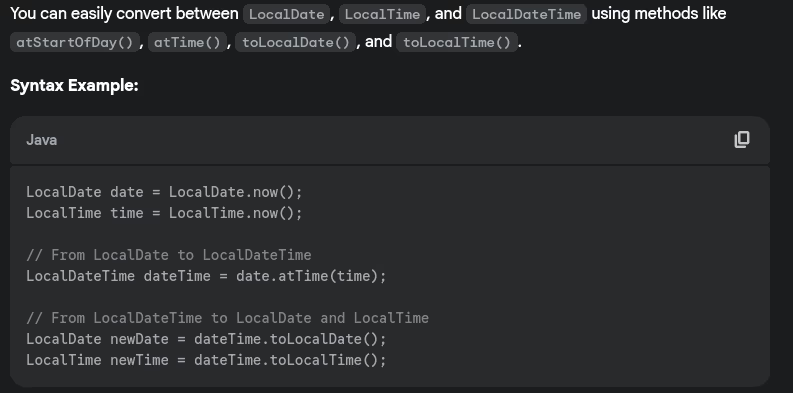
- How do you convert between different date-time classes?
Searching/Sorting
- When would you use binary search? What are its prerequisites?

- When would you use merge sort vs quick sort?

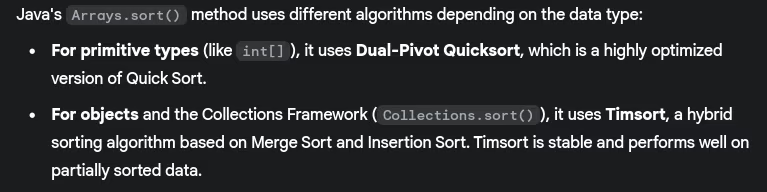
- What sorting algorithms does Java use internally?
- What’s the difference between stable and unstable sorting algorithms?


OOP
- Explain the four pillars of OOP with examples. Difference between them

- Difference between association, aggregation and composition

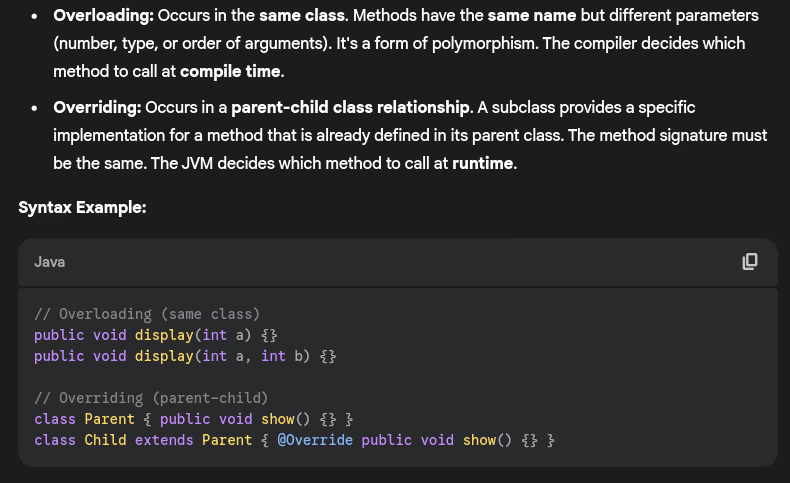
- What’s the difference between method overloading and method overriding?
- Can you override static methods? Why or why not?

- What’s the difference between abstract classes and interfaces?

- Explain the concept of polymorphism with a real-world example.
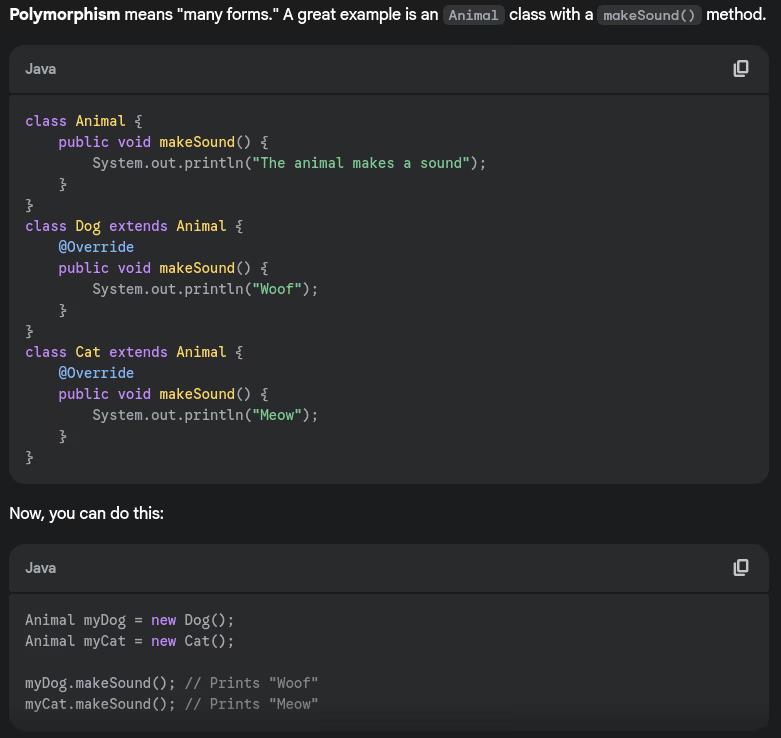
- Explain Encapsulation with a real-time example
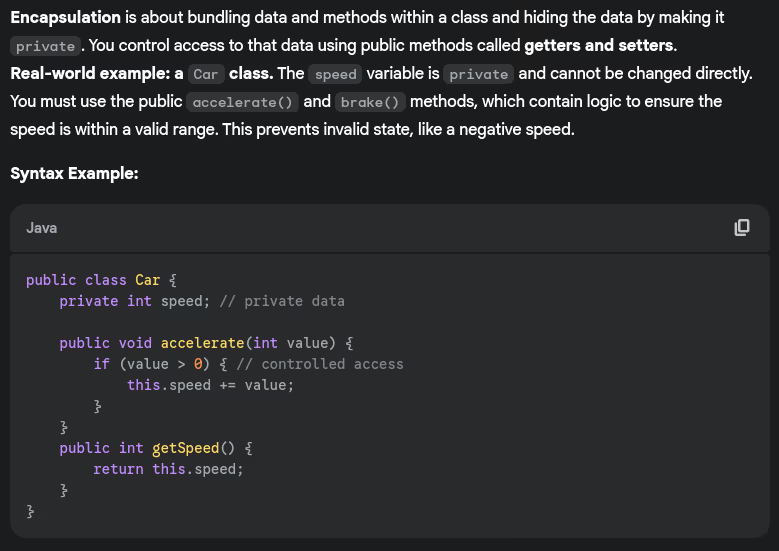
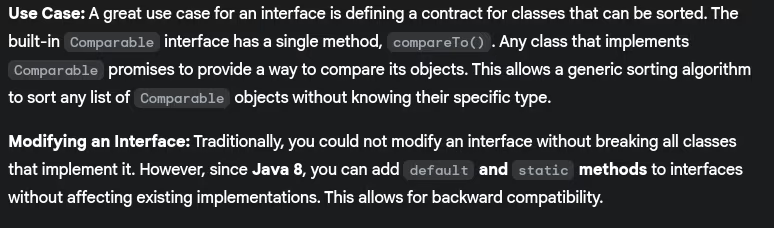
- Explain a real world use case of interface? Can we modify an interface after it has been created?
- What is Inheritance? Types of inheritance in Java

- What is Abstraction and how is it achieved in Java?

- What are access modifiers? Explain their scope.

- What’s the difference between
thisandsuperkeywords?
- Can a class extend multiple classes in Java? Why?

- What is method hiding vs method overriding?

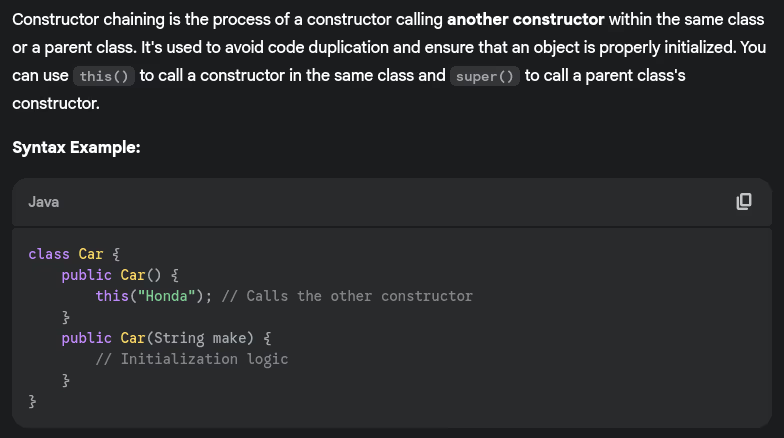
- Explain constructor chaining.
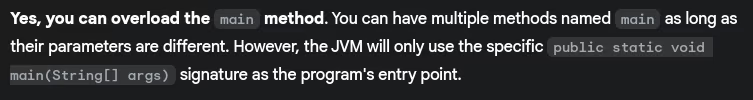
- Can you overload the main method in Java?
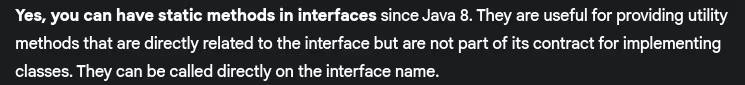
- Can we have static methods in interfaces?
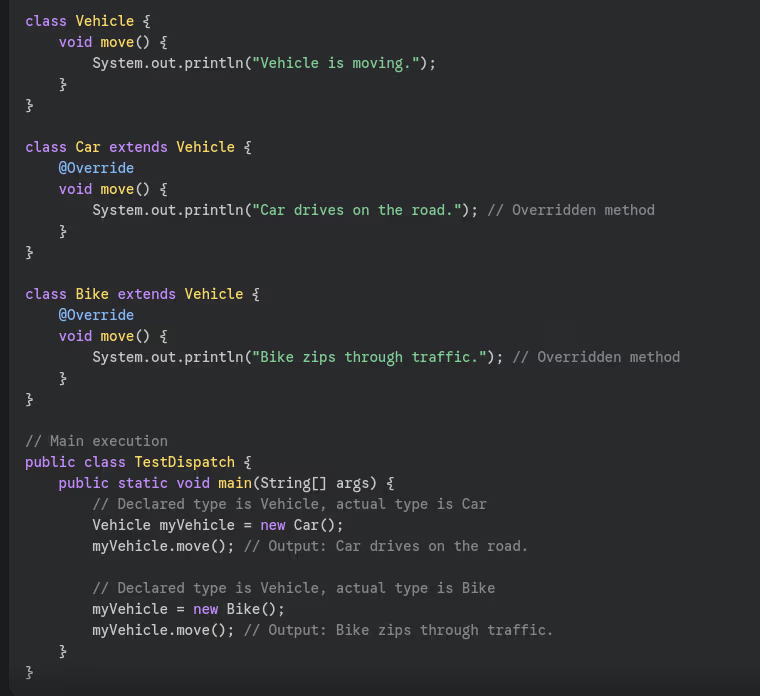
- What is dynamic method dispatch?

- Can we override private methods?

- What is a class and object in Java?

- Can we have private constructors?

- Difference between default constructor and parameterized constructor

- Can constructors be overloaded?

- What is constructor? Types of constructors

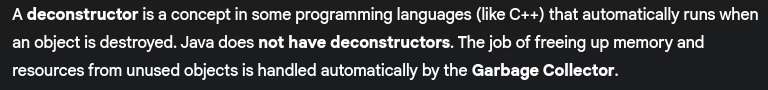
- What is deconstructor?
- Can we use both
this()andsuper()in the same constructor?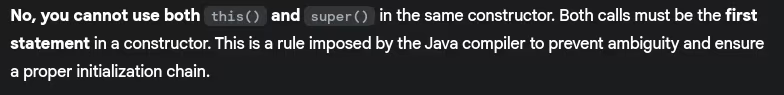
- Can abstract classes have constructors?

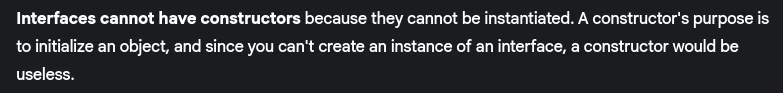
- Why can’t interfaces have constructors?
- What are default methods in interfaces (Java 8)?

- What is multiple inheritance and how is it achieved in Java?

- Why java is not pure oops based language?

Collections Framework
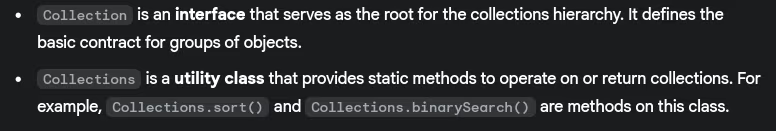
- Difference between Collection and Collections
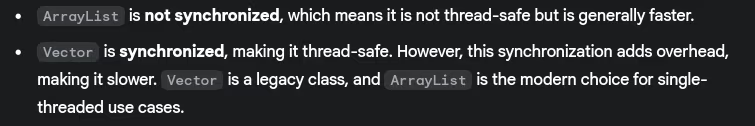
- Difference between ArrayList and Vector
- What is the initial capacity of ArrayList?

- How does
Collections.binarySearch()work?
- What’s the difference between
indexOf()andcontains()methods in collections?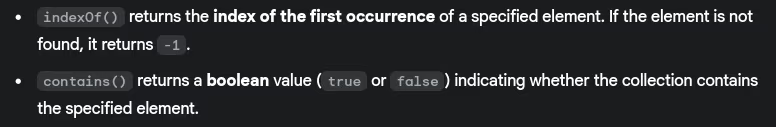
- How does
Collections.sort()work internally?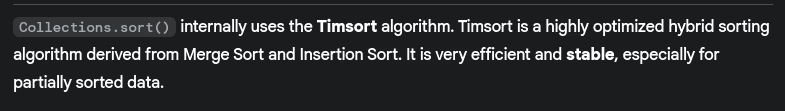
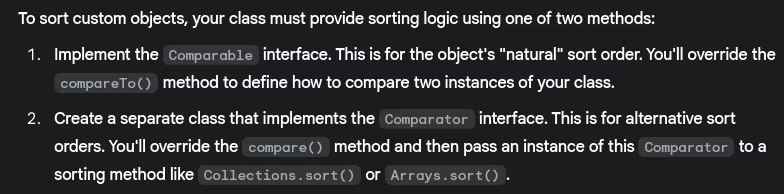
- How do you sort custom objects using
ComparableandComparator?
- What's the hierarchy of Collection framework? What is it?

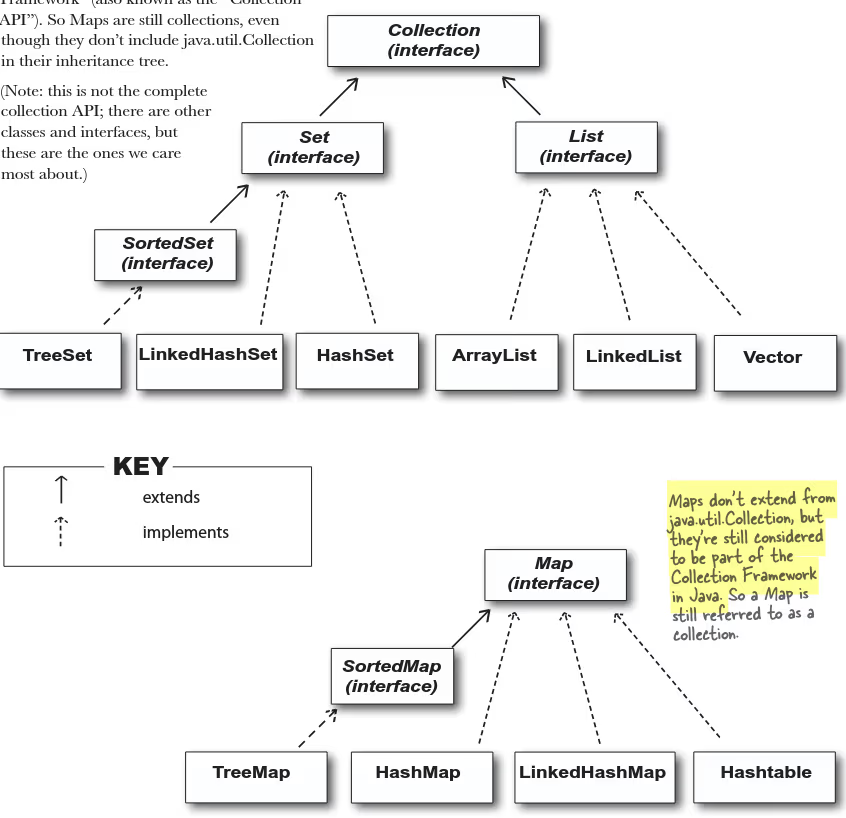
- Difference between
ArrayListandLinkedList? When to use which?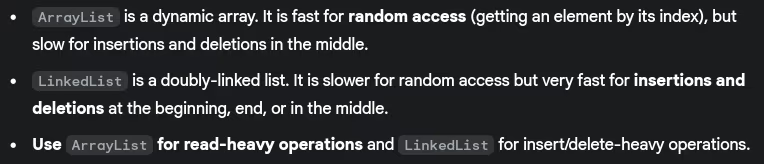
- How does
HashMapwork internally?
- What’s the difference between
HashMapandHashTable?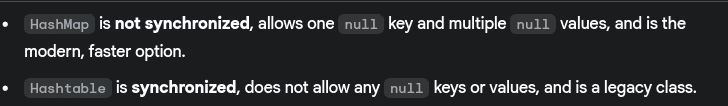
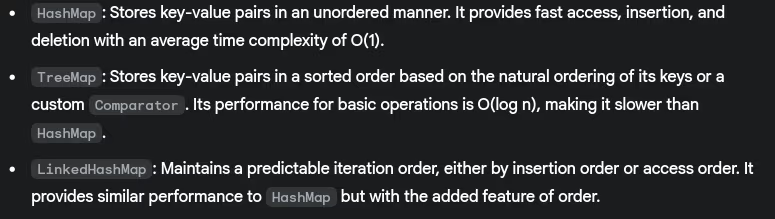
- HashMap vs TreeMap vs LinkedHashMap?
- HashSet vs TreeSet vs LinkedHashSet?

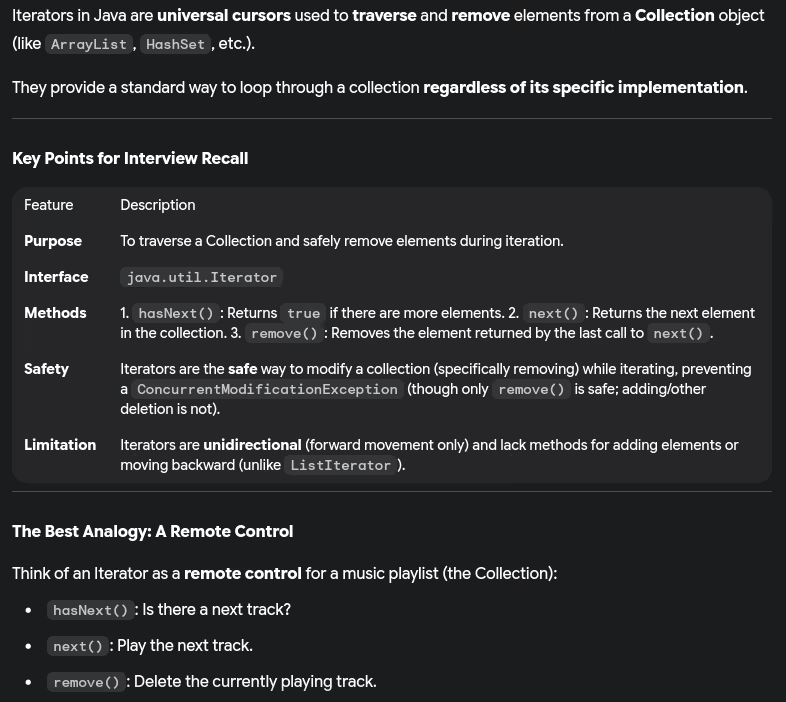
- What are iterators?
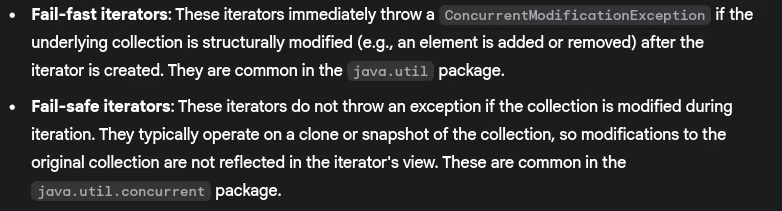
- What is fail-fast vs fail-safe iterators?
- Explain the difference between
Set,List, andMap.
- What are the different ways to iterate over a collection?

- How to sort custom objects?
- How does
HashSetensure uniqueness?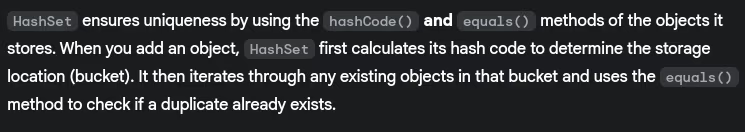
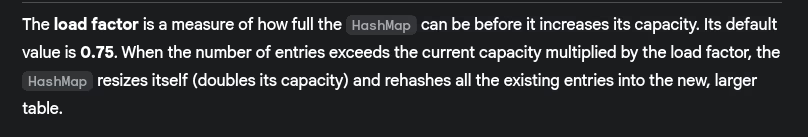
- What's the load factor in HashMap?
- Difference between
HashMapandConcurrentHashMap?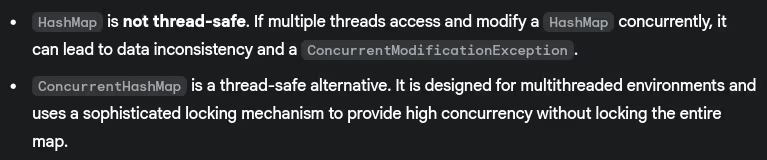
- What are generics in Java? Benefits?
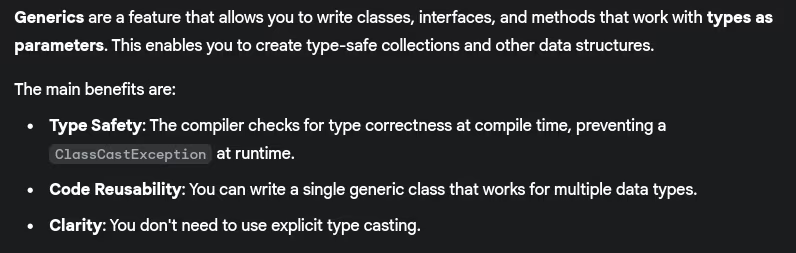
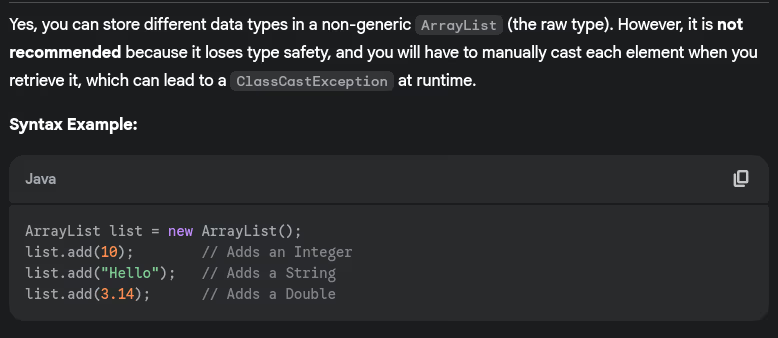
- Can we store different data types in ArrayList?
Functional Programming
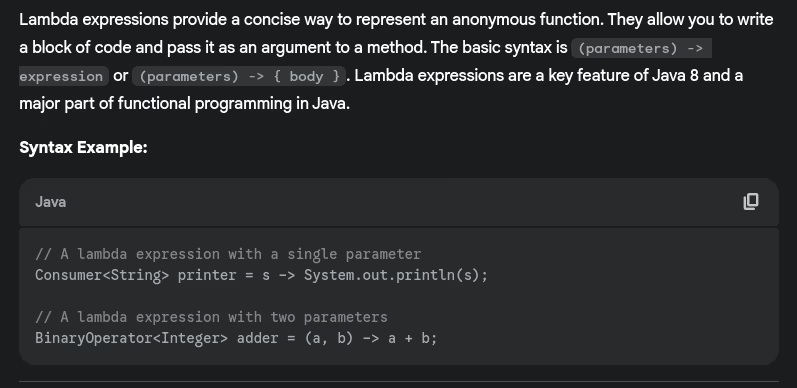
- What are lambda expressions? Provide syntax and examples.
- What are functional interfaces? Name some built-in ones.

- Can a functional interface have more than one abstract method?

- What's the difference between
Predicate,Function, andConsumerinterfaces?
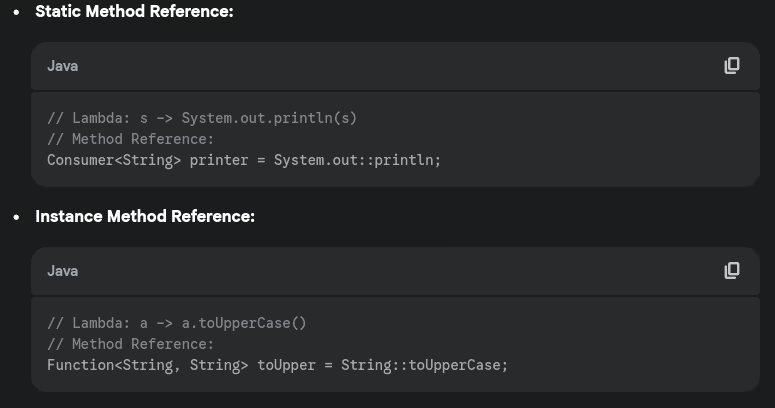
- What are method references? What are the different types?

- When would you use method references over lambda expressions?

- Write examples of static method reference and instance method reference.
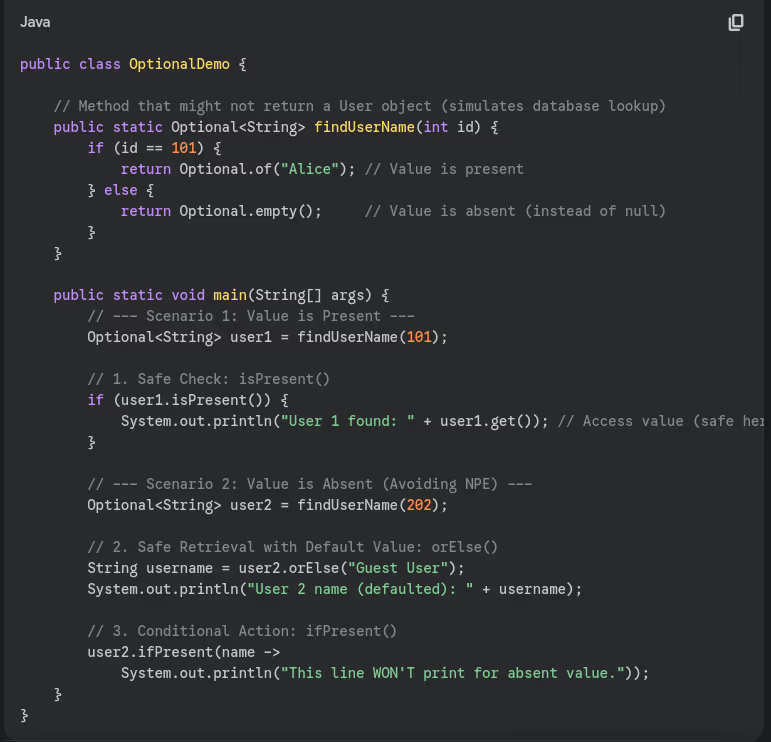
- What is
Optionalclass and why was it introduced?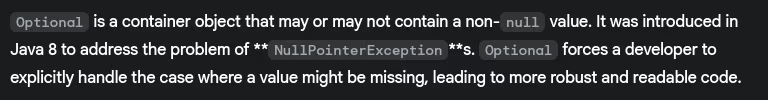
- How do you create Optional objects?
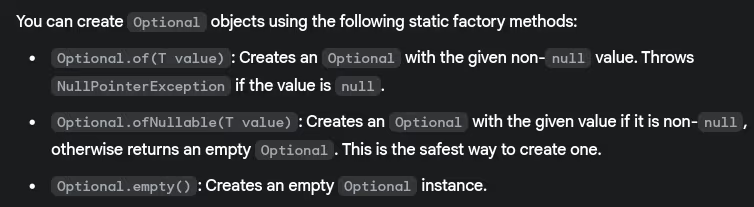
- What’s the difference between
orElse()andorElseGet()?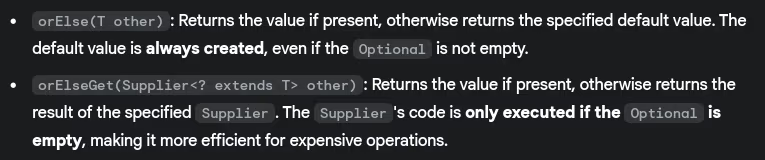
- When should you avoid using
Optional.get()?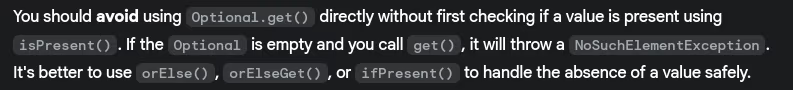
- What are Streams? How are they different from collections?

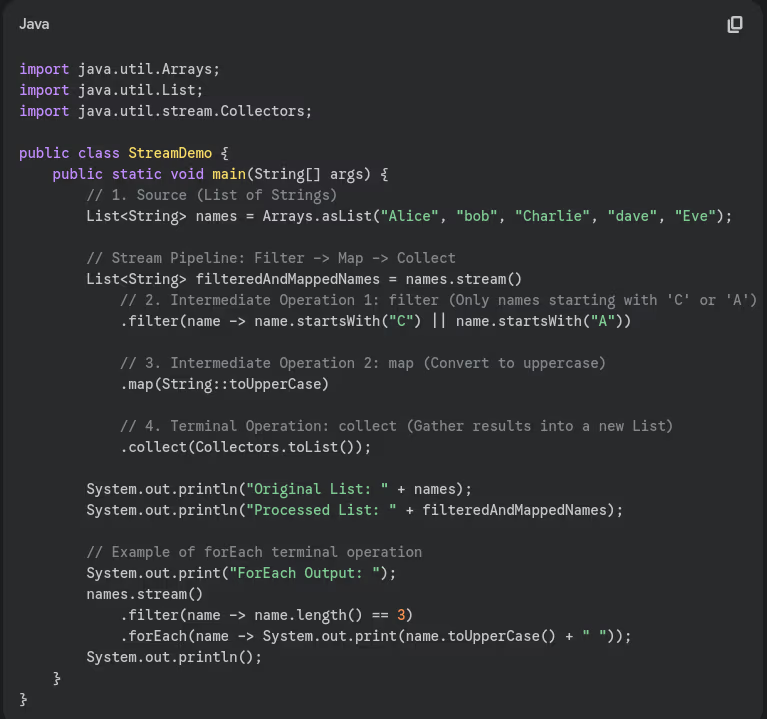
- What's the difference between intermediate and terminal operations?

- Explain lazy evaluation in streams.

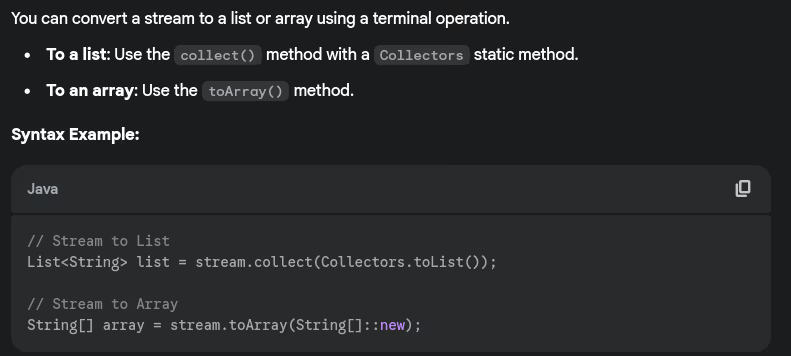
- How do you convert a stream to a list or array?
- What’s the difference between
map()andflatMap()?
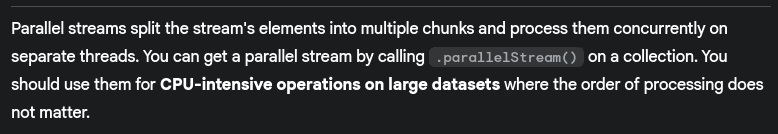
- How do parallel streams work? When should you use them?
- What’s the difference between
findFirst()andfindAny()?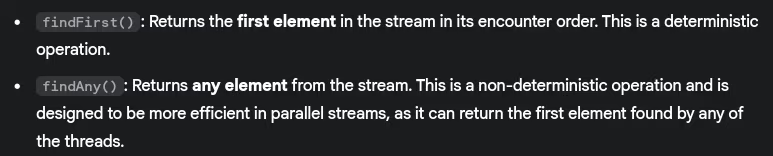
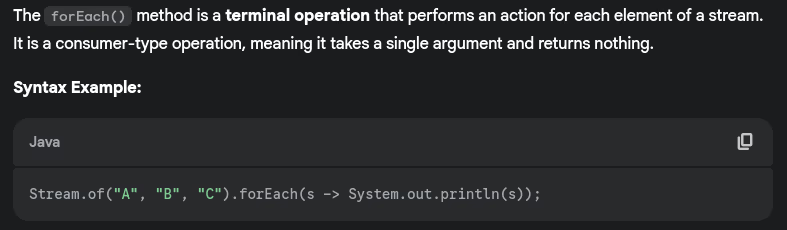
- What is forEach() method?
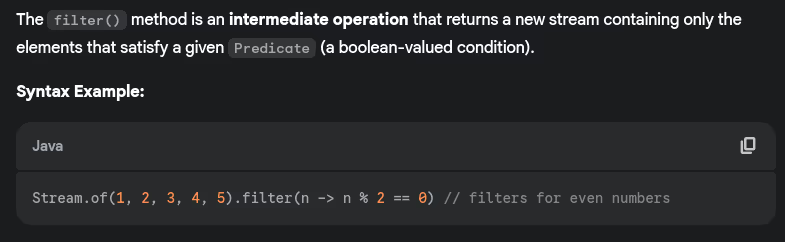
- What is filter() method in streams?
Exception Handling
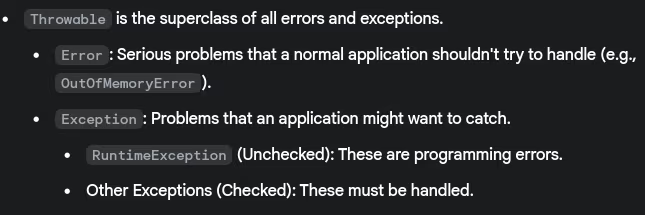
- What's the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions?

- Explain the exception hierarchy in Java.
- What happens if you use
returnstatement inside afinallyblock?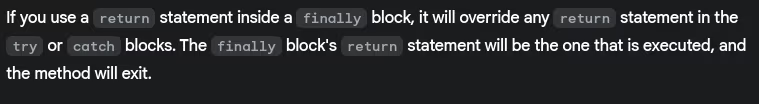
- What’s the difference between
throwandthrowskeywords?
- Can you have multiple catch blocks for a single try block?
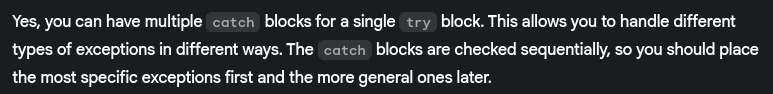
- What happens if an exception occurs in a
finallyblock?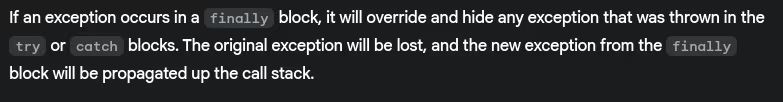
- What’s try-with-resources? Provide an example.
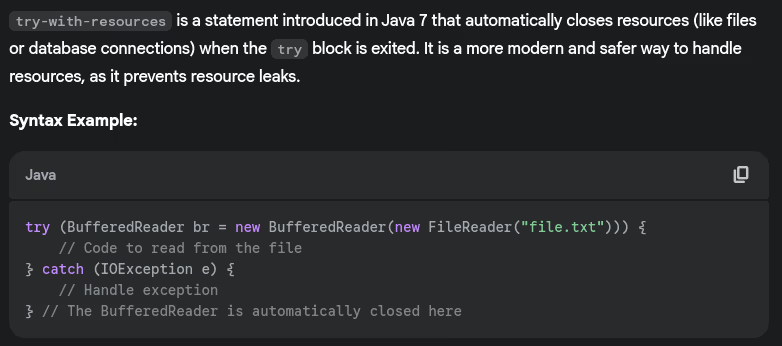
- Can you have a try block without catch or finally?

- What's the difference between
ErrorandException?
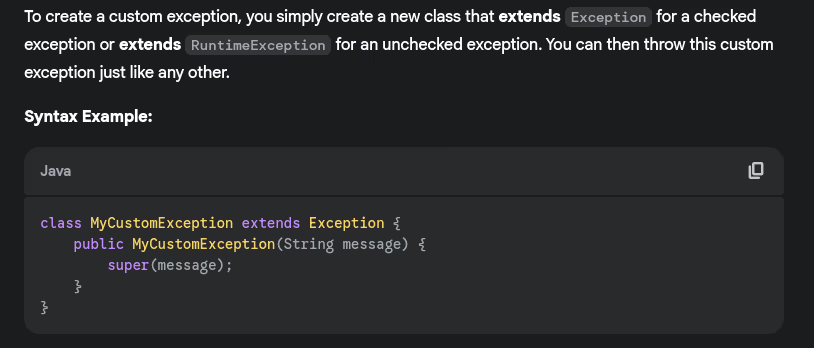
- How do you create custom exceptions?
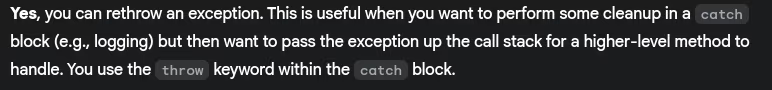
- Can we rethrow an exception?
- What is suppressed exception?

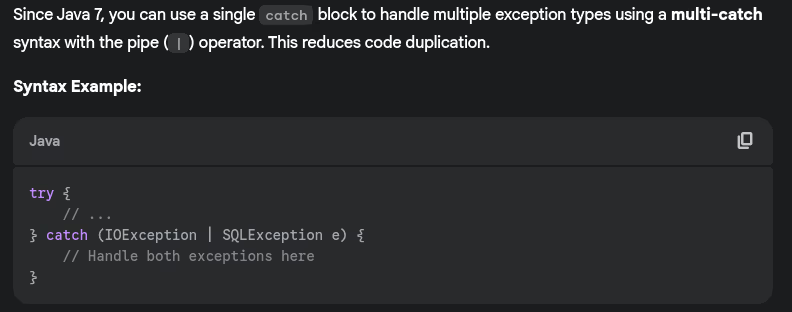
- How do you handle multiple exceptions in a single catch block?
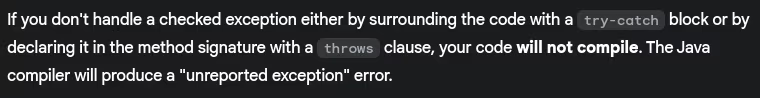
- What happens if you don’t handle a checked exception?
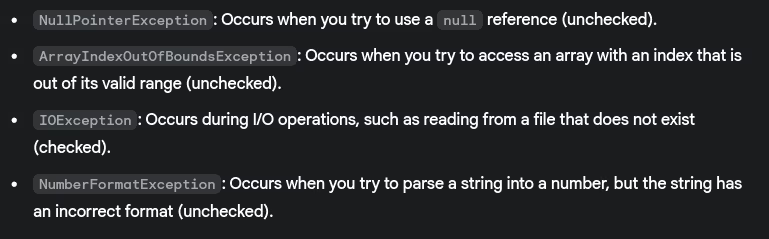
- What are some common exceptions and when do they occur?
Swing/GUI
- What is Java Swing?

- AWT vs Swing?

- Key components
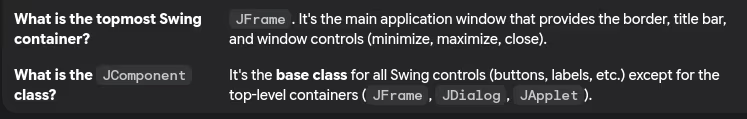
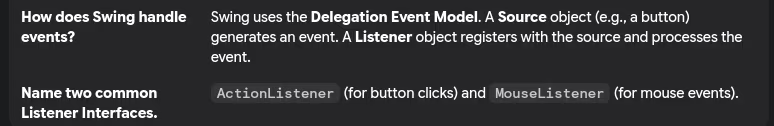
- Event handling
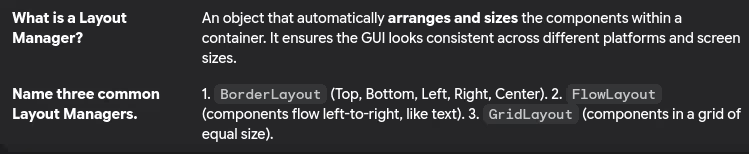
- Layout managers
Threading
- What is multithreading in Java?

- How do you create threads in Java?
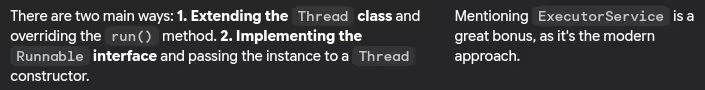
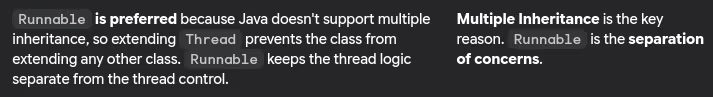
- Difference between extending Thread class and implementing Runnable
- What is the thread lifecycle?
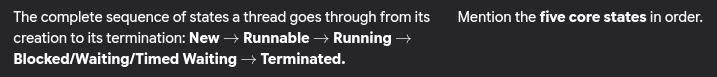
- What are different thread states?

- What is synchronization in Java?

- What is the synchronized keyword?

- Difference between synchronized method and synchronized block

- What is thread safety?

- What are race conditions?

- What is deadlock and how to avoid it?

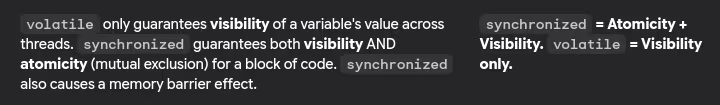
- What is volatile keyword and when to use it?
Circular transclusion detected: 03-Resources/Learn/Placement-Prep-Docs/Java-Interview-Questions
- Difference between volatile and synchronized
- What is ThreadLocal in Java?

- What are wait(), notify(), and notifyAll() methods?
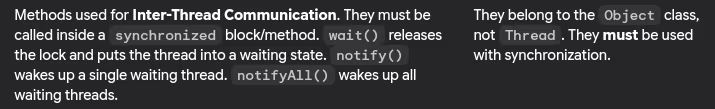
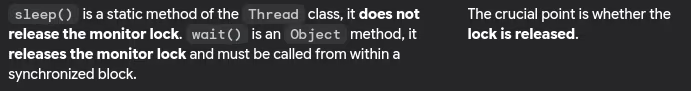
- Difference between sleep() and wait() methods
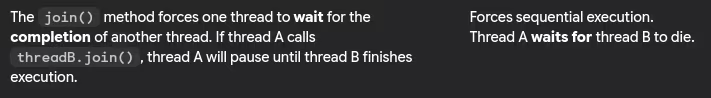
- What is join() method in threads?
- What is daemon thread?

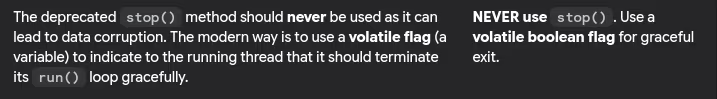
- How do you stop a thread in Java?
- What is thread pool and executor framework?
File Handling
Networking
Coding Questions
Reverse a String without Using Built-in Methods
public String reverseString(String str) {
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int left = 0;
int right = chars.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
char temp = chars[left];
chars[left] = chars[right];
chars[right] = temp;
left++;
right--;
}
return new String(chars);
}How to Check if Two Strings Are Anagrams
public boolean areAnagrams(String s1, String s2) {
if (s1.length() != s2.length()) {
return false;
}
char[] arr1 = s1.toCharArray();
char[] arr2 = s2.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(arr1);
Arrays.sort(arr2);
return Arrays.equals(arr1, arr2);
}Find the Second Largest Element in an Array
public int findSecondLargest(int[] arr) {
int largest = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int secondLargest = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int num : arr) {
if (num > largest) {
secondLargest = largest;
largest = num;
} else if (num > secondLargest && num != largest) {
secondLargest = num;
}
}
return secondLargest;
}Find Duplicate Elements in an Array
public void findDuplicates(int[] arr) {
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> duplicates = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : arr) {
if (!seen.add(num)) {
duplicates.add(num);
}
}
System.out.println("Duplicate elements: " + duplicates);
}Remove Duplicates from a List
public <T> List<T> removeDuplicates(List<T> list) {
return new ArrayList<>(new HashSet<>(list));
}Implement Binary search Algorithm
public int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
if (arr[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}Find First and Last Occurrence of an Element in a Sorted Array
public int[] findFirstAndLast(int[] arr, int target) {
int first = -1;
int last = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == target) {
if (first == -1) {
first = i;
}
last = i;
}
}
return new int[]{first, last};
}Implement Sorting Algorithms (Bubble Sort)
public void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}Check if a Number is even or Odd Using the Ternary Operator
public String checkEvenOdd(int num) {
return (num % 2 == 0) ? "Even" : "Odd";
}Print Prime Numbers between 1 to 100
public void printPrimes(int limit) {
for (int i = 2; i <= limit; i++) {
boolean isPrime = true;
for (int j = 2; j <= Math.sqrt(i); j++) {
if (i % j == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPrime) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}Find the Sum of Squares of even Numbers Using Streams
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public int sumOfSquaresOfEvens(int[] numbers) {
return IntStream.of(numbers)
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 0)
.map(n -> n * n)
.sum();
}Find Duplicate Characters in a String
public void findDuplicateChars(String str) {
Map<Character, Integer> charCount = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
charCount.put(c, charCount.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : charCount.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() > 1) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}Find the Intersection of Two Arrays
public int[] findIntersection(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : arr1) {
set1.add(num);
}
List<Integer> intersectionList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : arr2) {
if (set1.contains(num)) {
intersectionList.add(num);
}
}
return intersectionList.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();
}Sort a Map by Its Values
public <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Map<K, V> sortByValue(Map<K, V> map) {
return map.entrySet()
.stream()
.sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue())
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
Map.Entry::getKey,
Map.Entry::getValue,
(e1, e2) -> e1, LinkedHashMap::new));
}Count Frequency of Each Character in a String Using Streams
public Map<Character, Long> countCharacters(String str) {
return str.chars()
.mapToObj(c -> (char) c)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity(), Collectors.counting()));
}Count Vowels and Consonants in a String
public void countVowelsAndConsonants(String str) {
int vowels = 0;
int consonants = 0;
String vowelsStr = "aeiouAEIOU";
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isLetter(c)) {
if (vowelsStr.indexOf(c) != -1) {
vowels++;
} else {
consonants++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("Vowels: " + vowels + ", Consonants: " + consonants);
}Find the Factorial of a Number
public long factorial(int n) {
if (n < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number must be non-negative");
long result = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
return result;
}Generate Fibonacci Series
public void generateFibonacci(int n) {
int a = 0, b = 1;
System.out.print(a + " " + b + " ");
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
int next = a + b;
System.out.print(next + " ");
a = b;
b = next;
}
}Find a Palindrome Number
public boolean isPalindrome(int num) {
int originalNum = num;
int reversedNum = 0;
while (num > 0) {
int digit = num % 10;
reversedNum = reversedNum * 10 + digit;
num /= 10;
}
return originalNum == reversedNum;
}Count Digits in a Number
public int countDigits(long num) {
if (num == 0) return 1;
int count = 0;
while (num != 0) {
num /= 10;
count++;
}
return count;
}How to Find Armstrong Numbers
public boolean isArmstrong(int num) {
int originalNum = num;
int sum = 0;
int power = String.valueOf(num).length();
int temp = num;
while (temp > 0) {
int digit = temp % 10;
sum += Math.pow(digit, power);
temp /= 10;
}
return sum == originalNum;
}How to Find the Missing Number in an Array
public int findMissingNumber(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length + 1;
int totalSum = n * (n + 1) / 2;
int arraySum = 0;
for (int num : arr) {
arraySum += num;
}
return totalSum - arraySum;
}Generate Random Numbers in Java
import java.util.Random;
public int generateRandomNumber(int min, int max) {
Random random = new Random();
return random.nextInt(max - min + 1) + min;
}Check if a Year is a Leap Year
public boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0);
}Count Number of Words in a Sentence
public int countWords(String sentence) {
if (sentence == null || sentence.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
String[] words = sentence.trim().split("\\s+");
return words.length;
}Explain Tower of Hanoi
The Tower of Hanoi is a classic recursive puzzle. The goal is to move a stack of discs of different sizes from a source peg to a destination peg, with the help of an auxiliary peg. The rules are:
- Only one disc can be moved at a time.
- A larger disc can never be placed on top of a smaller disc.
- The top disc is the only one that can be moved.
The solution is recursive:
- Move
n-1discs from the source to the auxiliary peg. - Move the largest disc (
n) from the source to the destination peg. - Move the
n-1discs from the auxiliary to the destination peg.
Find if a String is Interleaved of 2 other Strings
public boolean isInterleaved(String s1, String s2, String s3) {
if (s1.length() + s2.length() != s3.length()) {
return false;
}
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[s1.length() + 1][s2.length() + 1];
dp[0][0] = true;
for (int i = 0; i <= s1.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= s2.length(); j++) {
if (i > 0 && s1.charAt(i - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] || dp[i - 1][j];
}
if (j > 0 && s2.charAt(j - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] || dp[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
return dp[s1.length()][s2.length()];
}